7 Website Localization Best Practices to Take Your Website Global
Learn effective methods to streamline website localization with these expert-validated best practices.

For companies with a presence in multiple countries, website localization is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. This comprehensive process involves much more than simply translating text; it means adapting your website to different regions’ cultural and linguistic preferences.
Knowing the best practices of website localization can help you avoid avoid costly errors and be the key to tapping into new markets and engaging with diverse audiences effectively. By localizing your website, you not only enhance user experience but also expand your customer base and strengthen your brand’s global footprint.
However, without careful management, the complex process can quickly become expensive and time-consuming due to the volume of content and the number of stakeholders involved.
Here at Milengo, we believe you shouldn’t have to break the bank or lose your sanity to achieve global success. That’s why we’ve developed a streamlined approach to website localization for our clients based on tried and tested best practices.

Did you know?
72.4% of global consumers prefer to buy products in their native language?* Moreover, companies that invest in localization see a 1.5x increase in their conversion rates.
Ready to tap into these opportunities? With over 30 years of localization experience, Milengo can help you navigate the complexities of website localization. From language selection to cultural adaptation, we’ll ensure your website resonates with global audiences.
Schedule a free consultation today and discover how our expertise can elevate your business to new heights.
Best practices for website localization
In this blog, we’ll guide you through seven proven best practices for website localization, that will enable you to streamline efforts while keeping costs in mind.

#1: Define your website localization strategy
Before diving in, it’s crucial to define your localization goals and target audience to prioritize your efforts. Here’s a framework to help you decide:
- Corporate growth plan: Which geographical markets are your company targeting in the coming year/s?
- Cultural proximity: Targeting countries with similar cultural backgrounds can ease the adaptation process.
- Language similarities: Prioritizing languages that are spoken across multiple target markets can streamline translation costs.
- Localization timeline: How much time do you have to launch your multilingual website pages? Express jobs are always charged at a premium.
- Localization budget: How much do you have to spend on translations, technical and layout updates, and tools? Do you have the capacity to manage a full-scale localization project in-house, or do you need to outsource?
The next step is to define key website pages. Look through the (planned) pages on your website and identify which ones contain critical information about your company and main product offerings. You can segment pages by the following:
- High-impact pages: These pages typically have a significant influence on conversion rates and brand reputation (such as your homepage, about us, and key product pages). Prioritize human marketing translations with SEO in mind for these pages.
- Low-impact pages: These pages receive minimal traffic and have a limited impact on conversions or brand reputation. Consider omitting translation or using machine translation for these pages.
- Exclusion pages: Not all content will be relevant for all language versions, and thus may not require localization.
Once you’ve identified your target markets and key pages, set clear goals for your localization efforts. Are you aiming to increase website traffic from specific regions, boost conversions, or raise brand awareness? Defining these goals will help you measure your success later.
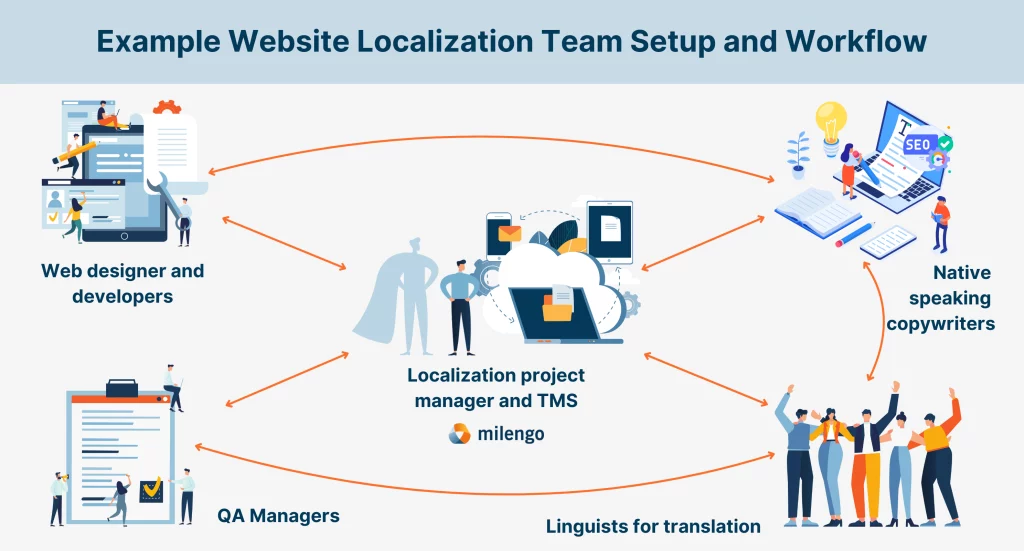
#2: Build your team and workflow
One of the many reasons website localization can be challenging is because it requires a team of specialists to ensure a smooth launch and subsequent maintenance. This includes web developers, graphic designers, copywriters, translators, quality assurance (QA) managers, and localization project managers.
When building your dream team, ask yourself about:
- Resource availability: What in-house team members or external resources do you currently have that could support the localization process? Will you need to outsource any roles?
- Content update frequency: How often will you need to make updates to your website? Will this be a one-off project, or will it require a dedicated team for regular content updates post-launch?
Qualified native-speaking translators are vital for successful website localization. They bring deep cultural insights and ensure your content resonates authentically with local audiences, avoiding miscommunications and enhancing engagement. Without their expertise, even the best localization efforts can miss the mark.
An experienced localization manager is also essential for streamlining the process, ensuring deadlines are met, and maintaining project efficiency.
Partnering with a translation service provider, like Milengo, grants you access not only to a network of expert native translators but also to experienced localization managers, minimizing obstacles and ensuring a seamless website localization rollout.
#3: Leverage time-saving translation tools
Nobody wants to spend hours sifting through email attachments or copying and pasting lines of translations into a content management system (CMS). The ultimate time-saving hack for localization projects is to automate processes with translation technology and tools.
A wide range of tools are available to manage localization projects and achieve your business goals. Here are some you can consider:
- Machine translation (MT): This can be used as a pre-translation tool to reduce costs for repetitive content and for content on low-impact pages. However, it must always be followed up with post-editing for accuracy and cultural sensitivity.
- Translation Memory (TM): Utilize a TM to store previously translated content. This ensures consistency and reduces costs when translating similar phrases across different pages, especially for technical information.
- Translation management systems (TMS): These powerful tools are a synergy of computer-assisted translation (CAT) tools and machine translation topped with project management and business intelligence features. They are made to be a centralized portal that helps you keep track of localization processes, workflows, communications, and costs.
Tip: If you decide to use a TMS, try to find one that integrates with your content management system for easy content export and re-importing of translations.
#4: Prep your website’s architecture
The architecture of your website can significantly impact the cost and efficiency of localization. Web development and design teams play a crucial role in this. They prepare your website for localization through a process called website internationalization. This involves ensuring your website’s architecture is flexible enough to accommodate multiple languages efficiently and cost-effectively.
Here’s what to consider:
- CMS Selection: A Content Management System (CMS) is the backbone of your website. Even if localization is only a later-stage plan, it is important to choose a CMS that supports multiple languages. This can save you time and resources down the line by eliminating the need to re-code parts of your website.
- Code structure: Ensure your website’s code is flexible enough to handle varying character lengths and that text can be easily resized as lengths of texts will change with translations. For example: German translations usually expand by 35% whereas Chinese translations contract. Encoding your site in Unicode (UTF-8) is also crucial to ensure it can accommodate special characters used in different languages.
- User interface design: A well-structured website from the start can significantly reduce localization costs. Review your website’s design elements. Are they adaptable for languages with different writing directions (e.g., right-to-left)? Where will you place the language switcher?

#5: Optimize technical SEO
A good international Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy is crucial for any website that wants to drive organic search internationally. There are three main building blocks of SEO: technical SEO, on-page SEO and off-page SEO.
Technical SEO optimizes your website for search engines to crawl, index, and rank it effectively. In simple terms, it’s how to help search engines find you.
Some key technical SEO considerations include:
- URL Structure: Implement clear and consistent URL structures that incorporate language codes to help search engines easily identify the language and regional differences.
- Hreflang Tags: Hreflang tags signal to search engines which language variation of your website is relevant to a specific user’s location.
- Localized Sitemaps: Create separate sitemaps for each language version of your website to help search engines index your content efficiently.
#6: SEO translation and cultural adaptation
Once you have all the systems in place, it’s finally time to start localizing your content! Localization goes beyond simple translation of words. It’s about cultural adaptation too. This means tailoring your content to resonate with local references, humor, and idioms of your target audiences.
Here’s how to approach this step:
- Keyword research: Use a keyword research tool to identify keywords relevant to the high-impact pages in your target markets. Your linguists will need to incorporate these keywords into translations in a natural-sounding way to help your localized website rank higher in local search engine results.
- Numbers and currencies: Localize details such as dates, times, number formats, currency symbols, and measurement units to prevent confusion.
- Images & colors: Localization is about visuals too. Using culturally appropriate images and graphics is key to building trust and engagement with your global audience.
- Translation quality: Invest in professional SEO translations by native speakers who understand both your industry as well as the nuances of the target language and culture. Ideally your linguists should also be seasoned marketing translators to ensure CTAs are well-written to drive conversion.
#7: Test, launch, promote and optimize
Before launching your localized website, thorough testing is crucial. This includes functionality testing across languages and meticulous proofreading by native speakers. Look out for things such as:
- Text fit: Ensure translations fit within the original page layout by reviewing them after importing them into your CMS. Translators often receive texts for translation with no visual context of where and how words are displayed and therefore might not always get the context right.
- Linguistic inconsistencies: Ensure consistent terminology, tone of voice, and grammar throughout the website. For languages with formal and informal registers, maintain consistency within each register.
- Translation quality: Does the quality of translations match your expectations? You might need to get a native-speaking colleague to help out with this part.
- SEO and keyword placements: Verify keywords are sufficiently and correctly placed on SEO pages and ensure meta descriptions are complete.
- Broken links: Scan your pages with the help of plugins or tools for any 404 errors.
Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for your website that align with your goals, and track them regularly to measure the effectiveness of your localization efforts. KPIs for website localization can include:
- Website traffic by region
- Conversion rates
- Bounce rates
- Keywords you are ranking for
Launch your localized website, promote it widely, and watch your global audience grow. Then analyze data around your KPIs to identify areas for improvement and optimize your website accordingly.
Tip: Set up your tracking before launching your multilingual websites to accurately measure your efforts.
Unlock new markets with website localization
Want to implement these best practices for your website localization project? Look no further! At Milengo, we understand the complexities of localizing websites. We can help you navigate every step of the process, from crafting a winning localization strategy to meticulous translation and SEO optimization.
Our team of experienced linguists and localization experts will ensure your website speaks directly to your target audience in each language, boosting your global brand presence and website conversions.
Ready to unlock the potential of a global market? Contact us today for a free consultation and see how our streamlined approach to website localization can help your business thrive!
*Source: CSA Research
Selected icons used on this page are from Freepik.com.
Ihr News Roundup zum Thema Lokalisierung
Unser Newsletter liefert brandaktuelle Infos und Tipps rund um Lokalisierung direkt in Ihr Postfach – unterhaltsam aufbereitet von echten Branchenexperten!
Calculate your REAL translation costs
Get free quote





